You can run this notebook in a live session or view it on Github.
Hindcast Predictions of Equatorial Pacific SSTs#
In this example, we evaluate hindcasts (retrospective forecasts) with HindcastEnsemble of sea surface temperatures in the eastern equatorial Pacific from CESM-DPLE. These hindcasts are evaluated against a forced ocean-sea ice simulation that initializes the model.
See the quick start for an analysis of time series (rather than maps) from HindcastEnsemble.
# linting
%load_ext nb_black
%load_ext lab_black
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import climpred
from climpred import HindcastEnsemble
import xarray as xr
xr.set_options(display_style="text")
# silence warnings if annoying
# import warnings
# warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
<xarray.core.options.set_options at 0x10d603d30>
We’ll load in a small region of the eastern equatorial Pacific for this analysis example.
initialized = climpred.tutorial.load_dataset("CESM-DP-SST-3D")["SST"]
recon = climpred.tutorial.load_dataset("FOSI-SST-3D")["SST"]
initialized
<xarray.DataArray 'SST' (init: 64, lead: 10, nlat: 37, nlon: 26)>
[615680 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
TLAT (nlat, nlon) float64 ...
TLONG (nlat, nlon) float64 ...
* init (init) float32 1.954e+03 1.955e+03 ... 2.016e+03 2.017e+03
* lead (lead) int32 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
TAREA (nlat, nlon) float64 ...
Dimensions without coordinates: nlat, nlonThese two example products cover a small portion of the eastern equatorial Pacific.
It is generally advisable to do all bias correction before instantiating a HindcastEnsemble. However, HindcastEnsemble can also be modified with HindcastEnsemble.remove_bias().
climpred requires that lead dimension has an attribute called units indicating what time units the lead is assocated with. Options are: years, seasons, months, weeks, pentads, days, hours, minutes, seconds. For the this data, the lead units are years.
initialized["lead"].attrs["units"] = "years"
hindcast = HindcastEnsemble(initialized).add_observations(recon)
hindcast
/Users/aaron.spring/Coding/climpred/climpred/utils.py:191: UserWarning: Assuming annual resolution starting Jan 1st due to numeric inits. Please change ``init`` to a datetime if it is another resolution. We recommend using xr.CFTimeIndex as ``init``, see https://climpred.readthedocs.io/en/stable/setting-up-data.html.
warnings.warn(
/Users/aaron.spring/Coding/climpred/climpred/utils.py:191: UserWarning: Assuming annual resolution starting Jan 1st due to numeric inits. Please change ``init`` to a datetime if it is another resolution. We recommend using xr.CFTimeIndex as ``init``, see https://climpred.readthedocs.io/en/stable/setting-up-data.html.
warnings.warn(
<climpred.HindcastEnsemble>
Initialized Ensemble:
SST (init, lead, nlat, nlon) float32 -0.3323 -0.3238 ... 1.179 1.123
Observations:
SST (time, nlat, nlon) float32 25.53 25.43 25.35 ... 27.03 27.1 27.05
Uninitialized:
None
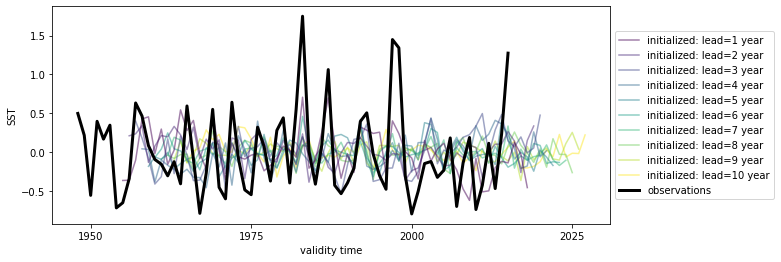
# Quick look at the HindEnsemble timeseries: only works for 1-dimensional data, therefore take spatial mean
hindcast.mean(["nlat", "nlon"]).plot()
<AxesSubplot:xlabel='validity time', ylabel='SST'>
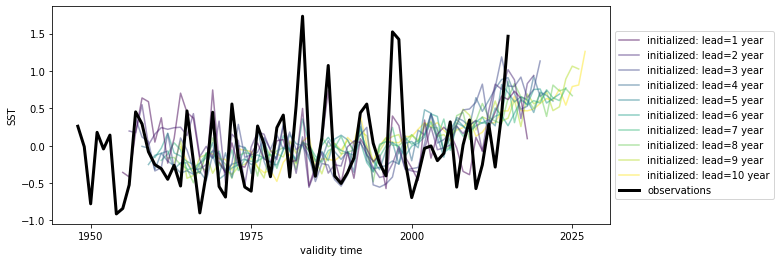
We first need to remove the same climatology that was used to drift-correct the CESM-DPLE.
recon = recon - recon.sel(time=slice(1964, 2014)).mean("time")
hindcast = hindcast.add_observations(recon)
hindcast.mean(["nlat", "nlon"]).plot()
/Users/aaron.spring/Coding/climpred/climpred/utils.py:191: UserWarning: Assuming annual resolution starting Jan 1st due to numeric inits. Please change ``init`` to a datetime if it is another resolution. We recommend using xr.CFTimeIndex as ``init``, see https://climpred.readthedocs.io/en/stable/setting-up-data.html.
warnings.warn(
<AxesSubplot:xlabel='validity time', ylabel='SST'>
We’ll also detrend climpred.stats.rm_trend() the reconstruction over its time dimension and initialized forecast ensemble over lead.
from climpred.stats import rm_trend
hindcast_detrend = hindcast.map(rm_trend, dim="lead_or_time")
hindcast_detrend.mean(["nlat", "nlon"]).plot()
<AxesSubplot:xlabel='validity time', ylabel='SST'>
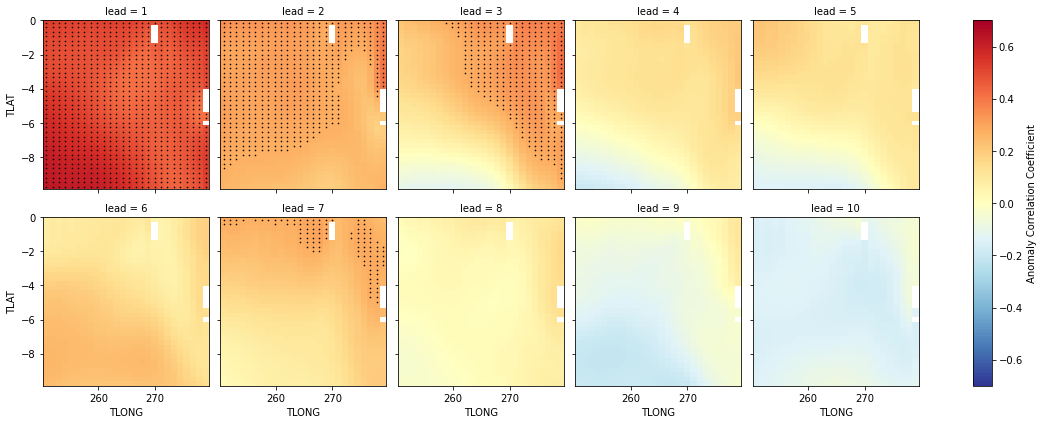
Anomaly Correlation Coefficient of SSTs#
We can now compute the ACC climpred.metrics._pearson_r() over all leads and all grid cells with HindcastEnsemble.verify.
predictability = hindcast_detrend.verify(
metric="acc", comparison="e2o", dim="init", alignment="same_verif"
)
predictability
<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (lead: 10, nlat: 37, nlon: 26)
Coordinates:
* nlat (nlat) int64 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ... 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
* nlon (nlon) int64 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ... 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
TLONG (nlat, nlon) float64 250.8 251.9 253.1 254.2 ... 276.7 277.8 278.9
* lead (lead) int32 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
TAREA (nlat, nlon) float64 3.661e+13 3.661e+13 ... 3.714e+13 3.714e+13
TLAT (nlat, nlon) float64 -9.75 -9.75 -9.75 ... -0.1336 -0.1336 -0.1336
skill <U11 'initialized'
Data variables:
SST (lead, nlat, nlon) float64 0.6272 0.6248 ... -0.05417 -0.05513
Attributes:
prediction_skill_software: climpred https://climpred.readthedocs.io/
skill_calculated_by_function: HindcastEnsemble.verify()
number_of_initializations: 64
alignment: same_verif
metric: pearson_r
comparison: e2o
dim: init
reference: []We use the pval keyword to get associated p-values for our ACCs. We can then mask our final maps based on 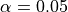 .
.
significance = hindcast_detrend.verify(
metric="p_pval", comparison="e2o", dim="init", alignment="same_verif"
)
# Mask latitude and longitude by significance for stippling.
siglat = significance.TLAT.where(significance.SST <= 0.05)
siglon = significance.TLONG.where(significance.SST <= 0.05)
p = predictability.SST.plot.pcolormesh(
x="TLONG",
y="TLAT",
col="lead",
col_wrap=5,
cbar_kwargs={"label": "Anomaly Correlation Coefficient"},
vmin=-0.7,
vmax=0.7,
cmap="RdYlBu_r",
)
for i, ax in enumerate(p.axes.flat):
# Add significance stippling
ax.scatter(
siglon.isel(lead=i), siglat.isel(lead=i), color="k", marker=".", s=1.5,
)
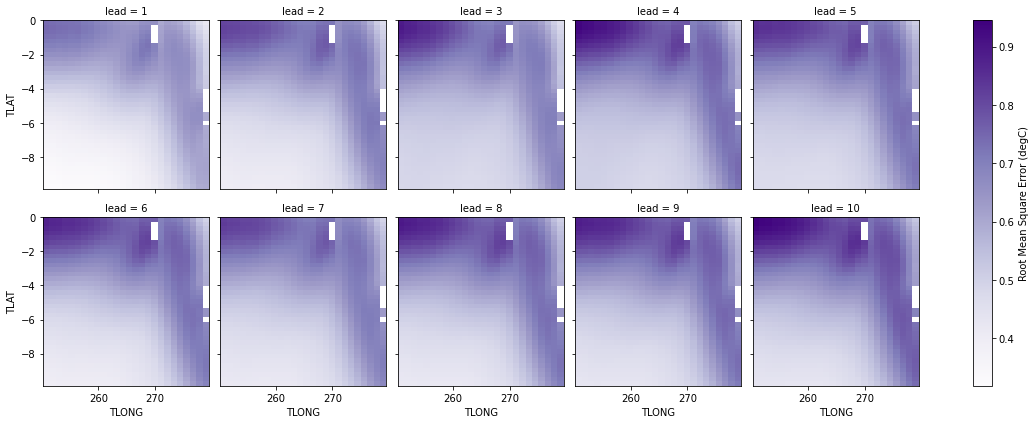
Root Mean Square Error of SSTs#
We can also check error in our forecasts, just by changing the metric keyword to _rmse() or _mae().
rmse = hindcast_detrend.verify(
metric="rmse", comparison="e2o", dim="init", alignment="same_verif"
)
p = rmse.SST.plot.pcolormesh(
x="TLONG",
y="TLAT",
col="lead",
col_wrap=5,
cbar_kwargs={"label": "Root Mean Square Error (degC)"},
cmap="Purples",
)